Projected EVM (Hedera) -> EVM Asset
Overview
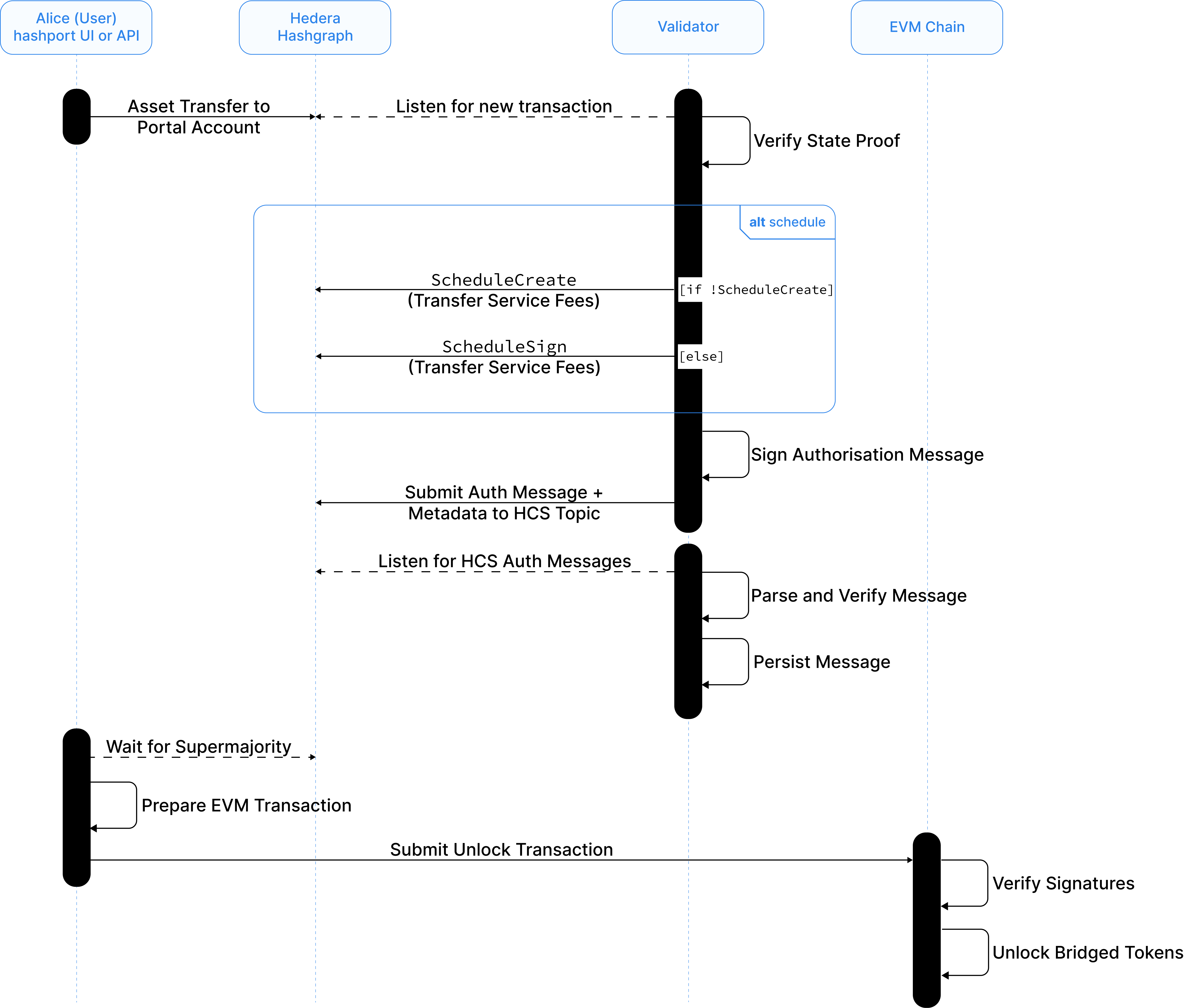
The transfer of HTS tokens mapped to ERC20 tokens from Hedera to the source EVM chain is described by the following sequence diagram.
Steps
1. Initiating the transaction
Alice uses the hashport Portal to transfer the mapped HTS tokens back to the EVM chain. She uses a software crypto wallet (e.g. MetaMask) or a wallet loaded directly on hashport to send a CryptoTransfer operation to the corresponding treasury account of the HTS tokens. In the memo of the transaction, a {chainId}-{receiving-address} is encoded where:
chainIdis the chain Id used in the EVM chainreceiving-addressis the EVM address that will receive the native EVM tokens.
2. Picking up the transaction
Validator nodes listen for new incoming transactions to the Treasury Account, which is reused for all hashport supported tokens. After receiving Alice's transaction, the nodes verify the state proof and validate that the memo contains a valid chain ID and EVM address.
3. Burning the tokens
Validators create a ScheduleBurn operation that removes the amount sent to the Treasury Account.
4. Complete the burning process and paying out fees
3.1 Each validator node creates a Schedule Transaction (ScheduleCreate) that transfers the service fee amount from the Fee Account to the list of validators equally.
3.2 Only one of these schedule transactions will be successfully submitted, creating a schedule entity. All other scheduled transactions will fail with IDENTICAL_SCHEDULE_ALREADY_CREATED error, and the transaction receipt will include the ScheduleID of the successfully submitted transaction.
3.3 All validators, except for the one that successfully submitted the transaction, will need to submit a ScheduleSign transaction. Once n out of m validators have signed the scheduled transaction, the scheduled transaction will be executed and the service fee will be sent out of the Fee Account. The amount of tokens defined in ScheduleBurn gets burned and the total supply of the HTS token in reduced.
You can learn more about Scheduled Transactions here.
5. Providing authorization signatures
Each validator node will need to sign the following authorization message: {hedera-tx-id}{router-address}{projected-token}{receiver}{amount} using their EVM-compatible private key. The message is then submitted to a topic in the Hedera Consensus Service.
6. Waiting for supermajority
Alice's hashport Portal waits for a supermajority of signatures, which is checked by watching the topic messages stream or fetched directly from the validator nodes.
7. Unlocking the EVM native tokens
Once supermajority is reached, the portal prompts Alice to submit an unlock transaction to the EVM chain. The transaction contains the raw data signed in the authorisation signatures, as well as the signatures. The smart contract verifies the authenticity of the signatures, charges the service fee and transfers the requested token to the specified receiving address.